The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0 is an updated version of the framework developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to assist organizations in managing and reducing cybersecurity risk. The framework is comprised of six core functions: Govern, Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
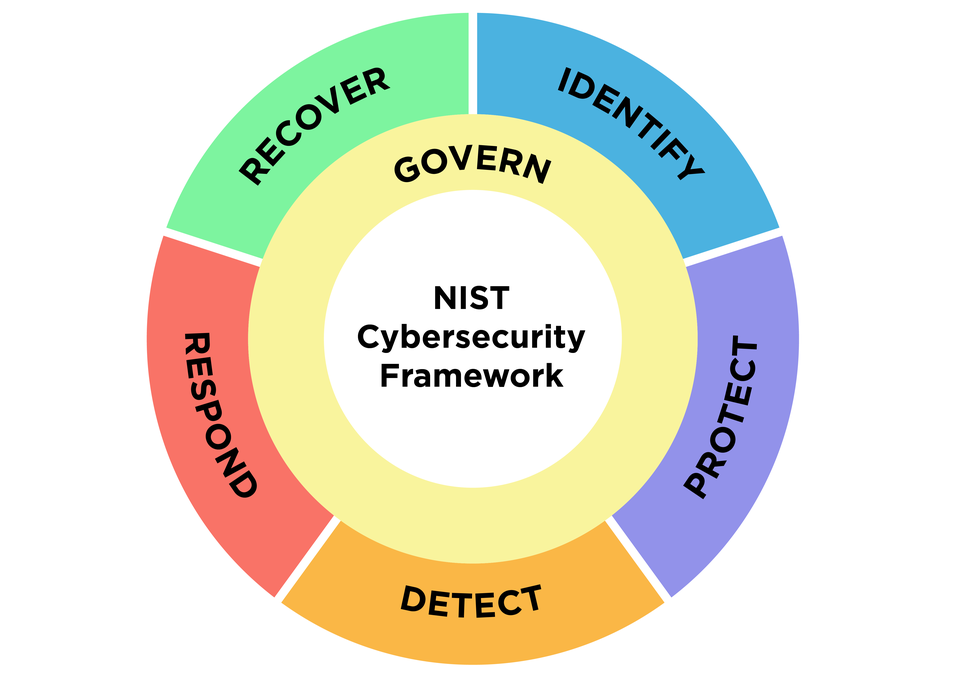
Govern
Establishes the organizational structures, policies, and processes needed to manage and oversee cybersecurity activities effectively. This function ensures that leadership is engaged, roles and responsibilities are defined, and cybersecurity efforts align with legal and regulatory requirements.
Identify
Focuses on understanding and managing cybersecurity risks to systems, assets, data, and capabilities. This involves asset management, risk assessments, and identifying vulnerabilities and threats to prioritize security measures.
Protect
Implements appropriate safeguards to ensure the delivery of critical services and to prevent or minimize the impact of cybersecurity incidents. This includes access control, data security measures, staff training, and maintenance of protective technologies.
Detect
Enables timely discovery of cybersecurity events through continuous monitoring and detection processes. This function involves implementing tools and procedures to identify anomalous activities or potential security breaches quickly.
Respond
Outlines actions to take once a cybersecurity incident is detected to contain its impact. This includes incident response planning, communication strategies, analysis, and mitigation efforts to manage and resolve incidents effectively.
Recover
Focuses on restoring systems and services affected by a cybersecurity incident to normal operation. It involves recovery planning, implementing improvements based on lessons learned, and coordinating with external parties as needed to resume regular activities promptly.
The NIS2 Directive Gap Assessment is a structured evaluation designed to help organizations manage and reduce cybersecurity risks in alignment with the European Union's updated Network and Information Security Directive (NIS2). The directive aims to strengthen cybersecurity resilience across the EU by imposing stricter security requirements on essential and important entities. The assessment focuses on key areas such as: Governance and Accountability, Risk Management Measures, Incident Reporting, Supply Chain Security, and Cooperation and Information Sharing.

Governance and Accountability
Establishes clear leadership responsibilities and oversight for cybersecurity within the organization. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, implementing policies and procedures, and ensuring top-level management is actively involved in cybersecurity decision-making processes.
Risk Management Measures
Focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating cybersecurity risks to critical assets and services. Organizations are required to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to manage risks, including regular security assessments and the adoption of security standards.
Incident Reporting
Mandates timely reporting of cybersecurity incidents to relevant authorities. This ensures rapid response and coordination in the event of a cyber incident, minimizing impact and facilitating information sharing about threats and vulnerabilities across sectors.
Supply Chain Security
Addresses the need for organizations to manage cybersecurity risks within their supply chains. This involves assessing third-party vendors, ensuring they meet security requirements, and incorporating security considerations into procurement and contract management processes.
Cooperation and Information Sharing
Encourages collaboration between organizations, sectors, and member states to enhance overall cybersecurity posture. This includes sharing threat intelligence, best practices, and participating in joint exercises to prepare for and respond to cyber threats collectively.
Cybersecurity Training and Awareness
Emphasizes the importance of cultivating a strong cybersecurity culture within the organization. This involves providing regular training and awareness programs for employees at all levels to recognize and respond appropriately to cybersecurity threats, thereby reducing human-related vulnerabilities.